FAQ
Self calibration easily done
Quality relevant test equipment
Within the framework of monitoring the accuracy of distance/angle measurements, the quality relevant test equipment must be monitored, maintained and calibrated in regular intervals. These calibrations must be retraceable to national standards and performed with the appropriate equipment.
Every company determines on its own, which tests are relevant to the quality of its products. The tests should be appropriate for the relevant process and serve to main-tain high and stable product quality.
Calibrate it yourself
The monitoring of Leica DISTO™ distance meters by ISO 900... : certified users.
Distance measurements:
You can perform the ISO 900... standard of requirements for monitoring distance meas-urements with the Leica DISTO™ on your own. Select a permanently constant and easy to access baseline of known length, from ap-prox. 1 to 10m (e.g. a window frame or the width of a room) and take at least 10 meas-urements (we recommend 20 measurements). The length the baseline must be determined with measuring equipment, e.g. a class II or I steel measuring tape approved by your national bureau of standards (Traceability to national standards. The class II or I Roman stamp is sufficient)
Calculation of the accuracy:
Determine the average of the measured values and calculate from it the systematic de-viation from the actual distance of the baseline. Then calculate the standard deviation according to the following formula:
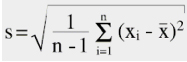
The typical accuracy of the meter is calculated by adding the systematic deviation to 2x the standard deviation. Calculation aid for Excel - please check the downloadable file (Calibration_aid.xls)
Approximation to the accuracy:
As an approximation to the calculated accuracy, just average the deviations of the mea-surements to the actual distance. This value must be within the specified typical accu-racy of the meter. Record the value and set the time for the next series of measurements. Repeat these check measurements regularly, especially before and after important measuring tasks. Mark the Leica DISTO™ with an”inspected” sticker and protocol the entire monitoring process. Please take the technical data and the clarifications to the measuring accuracy in the User Manual into account.
Angular measurements:
You can perform the ISO 900... standard of requirements for monitoring angular meas-urements with the Leica DISTO™ on your own.
To check the accuracy of the slope sensor in the 0° range, place the meter on a long spirit level (>1m), approved by your national bureau of standards (Traceability to the national standards). You can now determine the deviation of the Leica DISTO™ in re-gards to the laser beam or to the casing.
Calculation of the accuracy of the slope sensor in regards to the laser beam:
Align the spirit level, which serves as a base for the Leica DISTO™ to the horizontal as precisely as possible and project the height of the top surface of the spirit level with a second spirit level or leveling device to a vertical surface (e.g. a wall) from a distance of approx. 3-10m. Now take the height of the laser beam aperture above the casing of the Leica DISTO™ (16mm) into account and make the corresponding mark on the wall. Set the Leica DISTO™ on the spirit level and switch the meter to Pointing Mode. Underlay one end of the Leica DISTO™ until the center of the laser dot hits the mark on the wall Take at least 10 angle measurements (we recommend 20 measurements).
Determine the average of the measured values and calculate from it the systematic de-viation to the 0° angle. Then calculate the standard deviation according to the following formula:
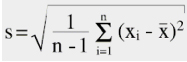
The typical accuracy of the meter in regards to the laser beam is calculated from the systematic deviation plus 2 x the standard deviation. Calculation aid for Excel - please check the downloadable file (Calibration_aid.xls)
Approximation to the accuracy:
As an approximation to the calculated accuracy, just average the measured values. This value must be within the specified typical accuracy of the meter.
Calculation of the accuracy of the slope sensor in regards to the casing:
Align the spirit level, which serves as the base for the Leica DISTO™ as horizontal as possible. Take at least 10 angle measurements (we recommend 20 measurements). To calculation the measurement deviation in regards to the casing, process analog to the calculation of the accuracy of the slope sensor in regards to the laser beam. Calculation aid for Excel - please check the downloadable file (Calibration_aid.xls). Record the value and set the time for the next series of measurements. Repeat these check measurements regularly, especially before and after important measuring tasks. Mark the Leica DISTO™ with an „inspected” sticker and protocol the entire monitoring process.
Please take the technical data and the clarifications to the measuring accuracy in the User Manual into account.
Should you want to check a random angle in regards to the casing, we recommend you use a so-called sine bar and spirit level that is as long as possible (>1m) as base. Both should be approved by your national bureau of standards (Traceability to the na-tional standards). Align the spirit level as precisely as possible to the horizontal. With the sine bar, any known angle can be precisely set. Set the meter on the sine bar and take at least 10 measurements of the same angle (we recommend 20 measurements).
To determine or evaluate the measured results, precede analog to the description of the distance measurements; by referencing the average value to the design value of the angle (predetermined with the sine bar).
Return to top
Return to FAQ